A soft conformable dressing that is effective against gram negative bacteria, gram positive bacteria and yeast. It contains the antimicrobial substance polyhexanide. The perforated wound contact layers contain a gentle silicone adhesive that provides secure, non-irritating adhesion and supports non-traumatic removal during dressing changes.
Moderately to heavily exuding acute or chronic wounds that are infected or at risk of infection, including surgical wounds, leg ulcers, diabetic foor ulcers, pressure ulcers


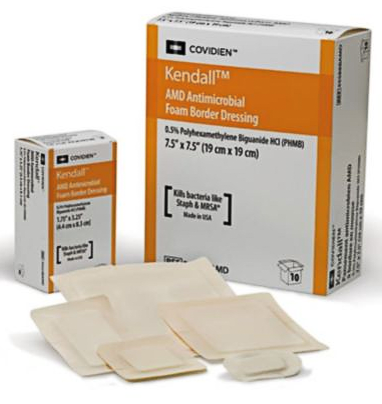
A sterile dressing containing the antimicrobial substance polyhexamethylene biguanide (Polyhexanide, polyhexanide), which kills bacteria and inhibits its growth. Polyhexanide released in the presence of wound exudate is an effective antimicrobial agent against a broad spectrum of microorganisms. Manages wound exudate and microbial contamination, reducing wound pain during healing. The perforated wound contact layer contains a gentle silicone adhesive that provides secure, non-irritating adhesion and supports non-traumatic removal during dressing changes. The low-friction, waterproof polyurethane film provides a bacterial barrier to the wound.